
This tells you if you could handle your current debts using only your most liquid assets—an important consideration if you ever face a cash crunch. Mortgages payable secure your business property with typically lengthy repayment liability account examples terms—often 15 to 30 years. The stability of these obligations can actually be a strength, providing predictable payment schedules while you build equity. Income taxes payable are calculated based on taxable income, incorporating relevant tax rates, deductions, and credits. For instance, the federal corporate tax rate in the United States is 21%, with state taxes adding to the burden.
- Another popular calculation that potential investors or lenders might perform while figuring out the health of your business is the debt to capital ratio.
- It signifies something that must be settled over time, typically through the transfer of economic benefits such as money, goods, or services.
- Understanding non-current liabilities is essential to assessing a business’s financial health and creditworthiness.
- A contingent liability would involve a potential loss to the business.
- It is essential for businesses to effectively manage their liabilities and maintain a healthy balance between debt and equity.
- Similarly, all other liabilities not required to be paid within the next 12 months shall be categorized as long-term liabilities.
Accrued Expenses

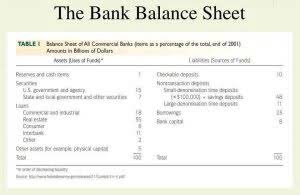
The amount of short-term debt— compared to long-term debt—is important when analyzing a company’s financial health. Interest PayableBusinesses and individuals often borrow money for short-term financing, which results in an obligation to repay the principal amount and interest. The portion of this debt representing the unpaid interest is considered an interest payable liability. This liability is also classified as a current liability since it is due within a year or the normal operating cycle. Non-current Liabilities – Also termed as fixed liabilities they are long-term obligations and the business is not liable to pay these within 12 months.
- Companies often negotiate favorable credit terms to extend payment periods, enabling them to allocate cash to other operational needs.
- The treatment of current liabilities varies by company and by sector and industry.
- Examples of current liabilities are accrued expenses, taxes payable, short-term debt, payroll liabilities, and dividend payables, among others.
- Examples of deferred unearned revenue include prepaid subscriptions, rent, insurance or professional service fees.
Best Internal Source of Fund That Company Could Benefit From (Example and Explanation)
Misclassifying current and long-term portions of debt distorts your liquidity ratios and can give management a false sense of short-term financial flexibility. This is particularly important if you have debt covenants tied to working capital or current ratios. One of the most dangerous pitfalls is failing to record all liabilities. This might sound obvious, but it’s surprisingly common – especially with verbal commitments or end-of-period expenses. Omitting liabilities doesn’t make them disappear; it just makes your financial statements misleading. By understanding what your accounting liability accounts really mean, you’ll make more informed decisions about financing, expansion, and overall business strategy.

Financial Close Solution
These liabilities reflect various forms of borrowed capital, such as bonds payable or mortgages, and can significantly impact a company’s long-term debt profile, cash flow, and interest expenses. Contingent liabilities are recorded to ensure the financial statements fully reflect the true position of the company at the time of the balance sheet date. Because a contingent liability has the ability to negatively impact a company’s net assets and future profitability, it should be disclosed to financial statement users if it is likely to occur.
Liabilities Explained
It is not classified as online bookkeeping a liability since it does not represent a future obligation. Unlike expenses, liabilities involve owed amounts that have yet to be paid. Current liabilities serve as a critical indicator of a company’s short-term solvency and its ability to generate enough cash to meet its obligations within the next twelve months.
- Below are some of the highlights from the income statement for Apple Inc. (AAPL) for its fiscal year 2024.
- A contra-liability account is a liability account in which the balance is expected to be a debit balance.
- Once declared, the amount becomes a liability until payment is made, usually within weeks.
- It is the total amount of salary expense owed to employees at a given time that has not yet been paid out by the company.
Accurately accounting for pension obligations can be complex and may require actuarial valuations to determine the present value of future obligations. The contra revenue account is a reduction from gross revenue, which results in net revenue. These transactions are reported in one or more contra revenue accounts, which usually have a debit balance and reduce the total amount of the company’s net revenue. Some of the liabilities in accounting examples are accounts payable, Expenses payable, salaries payable, and interest payable. Uncertain future obligations, also known as contingent liabilities, are potential financial responsibilities that depend on the outcome of a future event.
FAQs About Liabilities
It is a reduction from equity because it represents the amount paid by a corporation to buy back its stock. The contra account accounting reduces the total number of outstanding shares. The treasury stock account is debited when a company buys back its shares from the open market. Liabilities show what a business owes and when those payments are due.

These payments are crucial for maintaining beneficial marketing relationships. For example, a company owes $6,000 to a marketing partner for a campaign, payable within 90 days. HighRadius offers a cloud-based Record to Report Suite that helps accounting professionals streamline and automate the financial close process for businesses. We have helped accounting teams from around the globe with month-end closing, reconciliations, journal entry management, intercompany accounting, and financial https://jab.jabdigitals.com/bookkeeper-synonyms-antonyms-rhyming-words/ reporting.
